将字体进行缓存,优化网站速度
·798 words·2 mins
Table of Contents
看着现在动辄几兆的字体,在网页上使用会严重拖慢加载速度,有没有什么方法能够改善这种情况?
这时候我们就需要对字体进行优化了
对字体进行优化的方式有很多,比如:
- 分组加载字体
- 限制字体加载时间
- 队列加载
- 自定义字体显示
本文主要介绍如何通过缓存的方式优化字体加载
注:本文字体应用针对全站生效
0. 浏览器兼容性 #
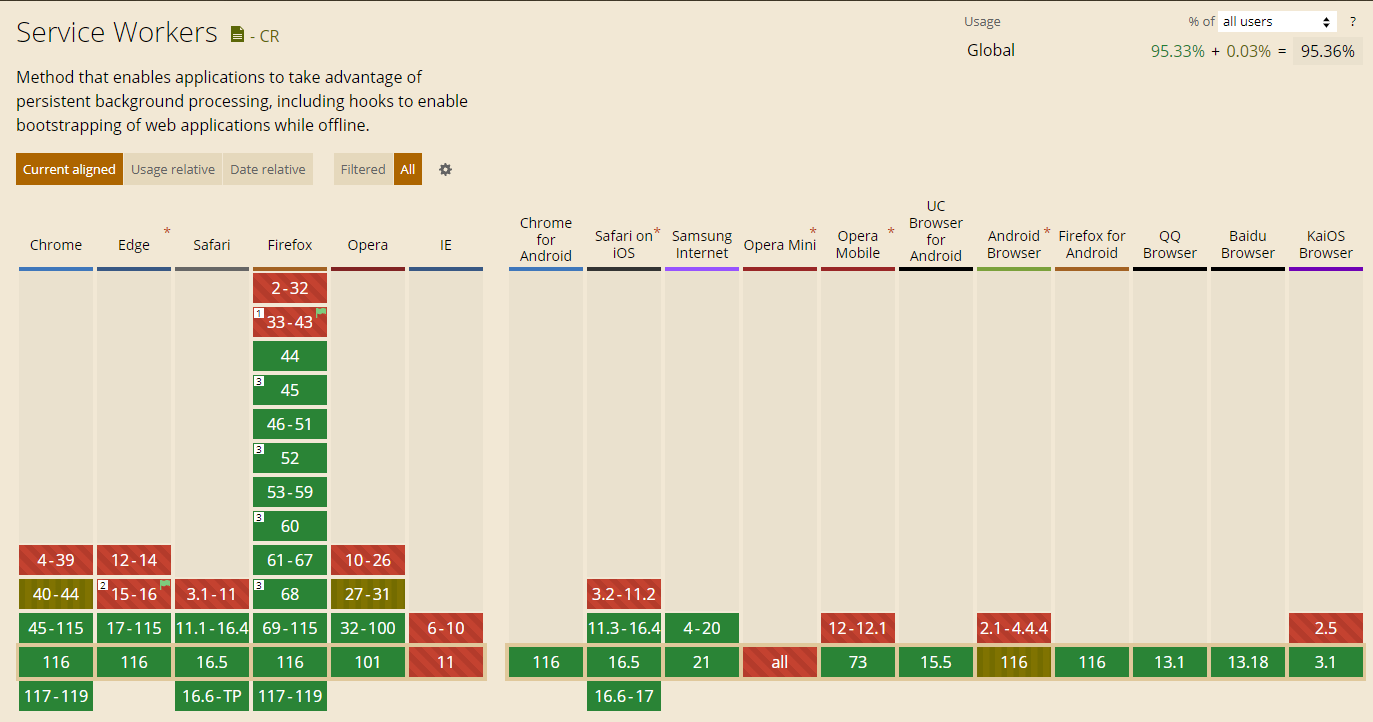
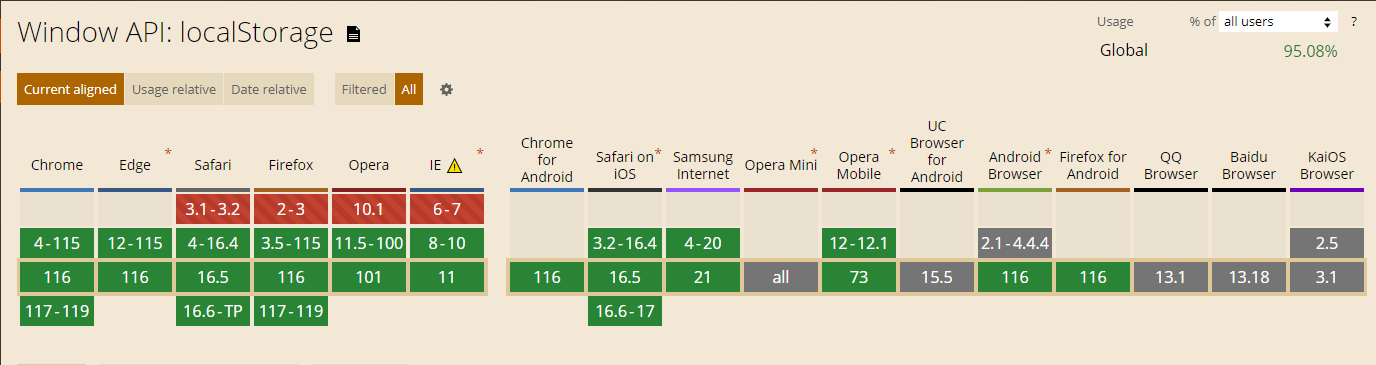
1. 使用 Service Worker 进行缓存 #
此方法的前提是你已经注册好了 Service Worker
// Service Worker 文件
// 此处将文件路径修改为实际路径
const fontFiles = [
'/path/to/font.woff2',
'/path/to/font.woff',
'/path/to/font.ttf',
];
self.addEventListener('install', event => {
event.waitUntil(
caches.open('font-cache')
.then(cache => cache.addAll(fontFiles))
);
});
self.addEventListener('fetch', event => {
event.respondWith(
caches.match(event.request)
.then(response => {
if (response) {
return response;
}
return fetch(event.request)
.then(response => {
const clonedResponse = response.clone();
caches.open('font-cache')
.then(cache => cache.put(event.request, clonedResponse));
return response;
});
})
);
});
// 注册文件
...
// 此处请根据需要添加要在网页中使用的字体名称
document.body.style.fontFamily = 'CustomFont';
2. 使用 Web Storage API 进行字体缓存 #
function isFontCached() {
return localStorage.getItem('cachedFont') === 'true';
}
function cacheFont() {
localStorage.setItem('cachedFont', 'true');
}
function loadFont() {
// 此处请根据需要添加要在网页中使用的字体名称
document.body.style.fontFamily = 'CustomFont';
}
if (isFontCached()) {
console.log('%c字体缓存: Existence', 'color: green; font-weight: bold;');
loadFont();
} else {
console.log('%c字体缓存: Missing', 'color: red; font-weight: bold;');
console.log('%c字体缓存机制: Caching', 'color: blue; font-weight: bold;');
cacheFont();
loadFont();
console.log('%c字体缓存机制: Success', 'color: green; font-weight: bold;');
}
@font-face {
font-family: CustomFont;
font-display: optional;
/* 此处将文件路径修改为实际路径 */
src: url("/path/to/font.ttf");
}
注:使用 localStorage 进行字体缓存仅适用于较小的字体文件,因为 localStorage 和 IndexedDB 的存储容量有限
如果字体文件较大,可能会导致存储空间不足或性能问题。
这种方法也无法享受到 Service Worker 提供的离线缓存和自动更新的功能,如果你的环境支持 Service Worker,推荐使用 Service Worker 缓存方案
3. 两种方法的不同 #
| Service Worker 缓存字体 | IndexedDB/LocalStorage 缓存字体 | |
|---|---|---|
| 功能和用途 | 提供高级缓存控制和离线支持 | 简单的数据存储和访问 |
| 存储位置 | 浏览器的缓存存储 | 浏览器的客户端存储 |
| 控制灵活性 | 高 | 低 |
| 离线支持 | 是 | 否 |
| 数据类型 | 二进制数据 | 字符串数据 |
| 功能复杂性 | 高 | 低 |
| 适用场景 | 高级缓存需求、离线访问 | 简单的数据缓存需求 |
| 字体大小 | 可缓存较大字体 | 仅缓存较小字体 |